Filing a Lawsuit Against an Uninsured Driver

I filed a lawsuit against what appears to be an uninsured driver this weekend. The Jefferson County Clerk has set it up so I can file a Complaint, the document that starts a lawsuit electronically from my computer. However, the filing fee for a lawsuit tends to cost me about $198 for each lawsuit filed with the Jefferson Circuit Court. The question is did I waste my money filing a lawsuit against an uninsured driver?
According to the Insurance Information Institute, about 11.5% of Kentucky motorists were, in violation of Kentucky, driving without insurance on their automobile. For Indiana, the rate was closer to 16.7%. https://www.iii.org/fact-statistic/facts-statistics-uninsured-motorists. So when a car accident or a motorcycle wreck occurs, one of the first questions a personal injury attorney has to deal with is whether the at-fault driver, or the vehicle they were operating, was insured.
The easiest way to find insurance coverage on an at-fault driver is hope that the police report has the proper insurance company listed. If that does not work, I will typically run the license plate of the at-fault vehicle with the Jefferson County Clerk. The Clerk can provide me with the insurance company and policy number the last time that vehicle was registered.
As a last resort, I will send the driver and owner of the at-fault vehicle a letter asking for their insurance information and threatening to file a lawsuit if they do not cooperate. The problem is filing a lawsuit against an uninsured driver may not be worth the time and expense involved.
Recall that a Judgment is really just a piece of paper that says someone owes you money. So, in essence, a Judgment against someone can be worthless if they have no assets to collect it against or if they can bankrupt that Judgment by filing Bankruptcy proceedings. So for the personal injury suits I filed, it could be that we won’t even recover the filing fee much less the value of the client’s personal injury claim. Granted, in Kentucky, K.R.S. 187.410 allows me to revoke someone’s driving privileges if the unpaid Judgment relates stems from a car wreck. However, if the at-fault driver files Bankruptcy, the suspension, and my client’s Judgment, is dissolved.
Nevertheless, I believe this instance justified a personal injury lawsuit. My injured client had an initial Emergency Room bill in excess of $19,000 and he may not have had uninsured motorist coverage either. As a result, unless I can find insurance coverage on the at-fault driver, my client really has no source to recover his pain and suffering claim from.
However, in this instance, my first goal is not to recover the value of his personal injury but rather, to keep my client from owing a large amount of medical expenses for a car wreck that was not his fault.; to do that, I’m going against the odds and hoping that filing a lawsuit against an uninsured driver will discover insurance coverage not readily apparent.
So what’s my fallback position(s) for everything? If all else fails, I will have to use health insurance to pay the medical bills. My client appears to be qualified for Medicaid after the car wreck occurred. While Medicaid will have a right to recover whatever medical expenses they pay out through what is known as subrogation claim or a right of reimbursement, they can only recover the amount that is actually paid to satisfy the $19,000 medical expense. My hope is that the amount Medicaid seeks to recover will be about one-third of the $19,000 expense. This way, I can reserve my client’s no-fault coverage of $10,000 and use that no-fault, a.k.a. as PIP coverage, to satisfy Medicaid’s subrogation claim.
Yes, in this worst-case scenario, regardless of the personal injury lawsuit, the client can not recover any more towards the value of his personal injury because the at-fault drive was uninsured and he did not purchase uninsured motorist coverage before the car wreck. However, in Kentucky, 99% of the time you are entitled to no-fault benefits of at least $10,000 as long as the car wreck happened in Kentucky and you were not driving a vehicle you owned that was uninsured.
As a result, this no-fault coverage may be the only insurance coverage that exists for this car wreck. Consequently, we have to stretch that $10,000 in no-fault coverage in every way possible so that the client, while uncompensated for his personal injury claim, will not owe medical bills for a car wreck that he did not cause.
At the end of the day, filing a lawsuit against an uninsured driver at least provides valuable information to determine my client’s best options.

 One of the leading causes of death among those between the ages of 1 and 54 in the United States is
One of the leading causes of death among those between the ages of 1 and 54 in the United States is 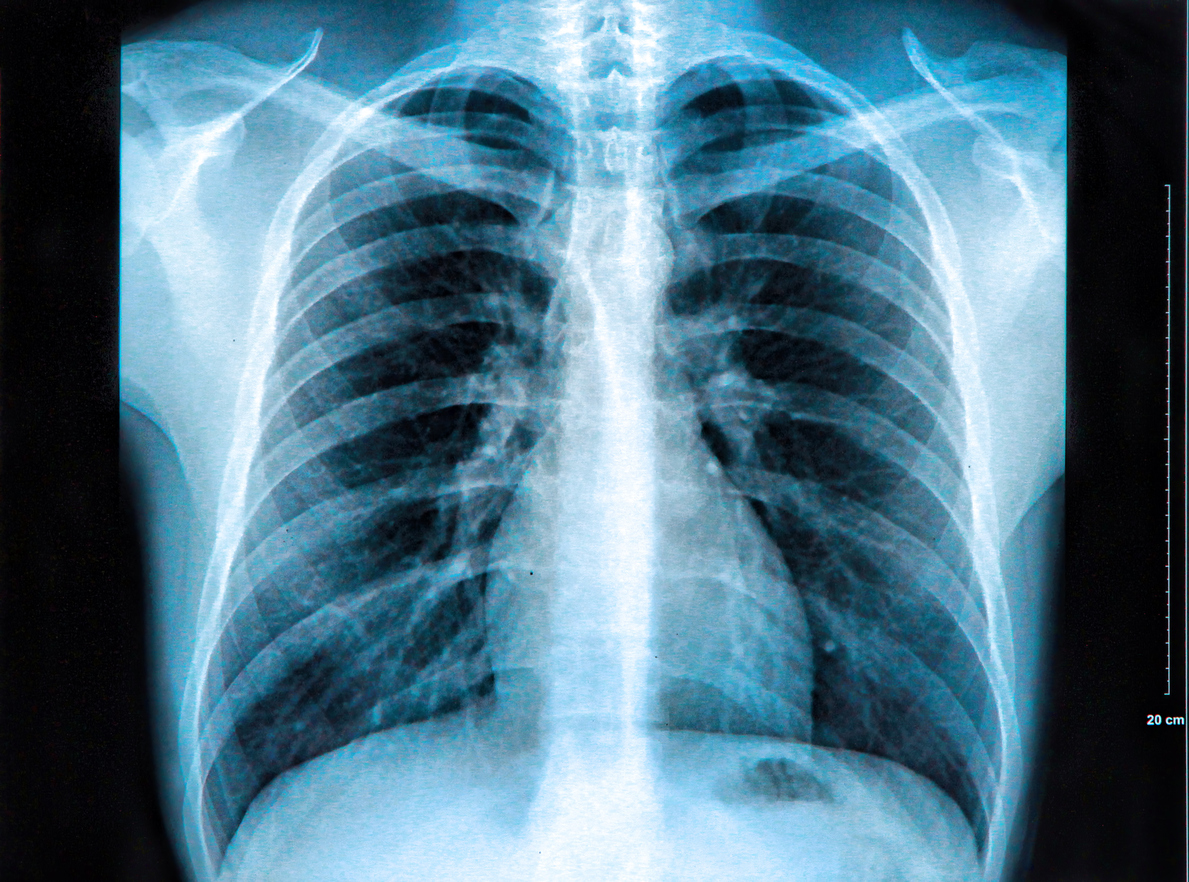 The most common injury sustained from blunt trauma to the chest is rib fractures and account for more than half of all thoracic injuries from non-penetrating trauma. Whereas in the elderly the most common cause of rib fractures is a fall and in youth the most common cause is recreational or athletic activities, in adults,
The most common injury sustained from blunt trauma to the chest is rib fractures and account for more than half of all thoracic injuries from non-penetrating trauma. Whereas in the elderly the most common cause of rib fractures is a fall and in youth the most common cause is recreational or athletic activities, in adults,  What is Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)? After someone goes through a traumatic event or life threatening situation it is not uncommon for that person to experience anxiety, flashbacks of the event, nightmares, increased jumpiness, etc. This has often been associated with war veterans or persons who have been physically or sexually assaulted, however, it’s also possible someone to experience PTSD after a
What is Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)? After someone goes through a traumatic event or life threatening situation it is not uncommon for that person to experience anxiety, flashbacks of the event, nightmares, increased jumpiness, etc. This has often been associated with war veterans or persons who have been physically or sexually assaulted, however, it’s also possible someone to experience PTSD after a  Have you been in an car accident? Are you experiencing neck or back pain? Maybe you’ve been diagnosed with a cervical, thoracic or lumbar strain/sprain. What is the difference between the types of sprains and strains?
Have you been in an car accident? Are you experiencing neck or back pain? Maybe you’ve been diagnosed with a cervical, thoracic or lumbar strain/sprain. What is the difference between the types of sprains and strains?